-
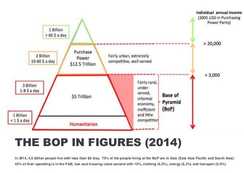 The Bottom of the Economic Pyramid or Base of the Economic Pyramid (BoP) is defined as those people whose earning is less than US$8 per day. This domain is popularly referred as Base of Pyramid (BoP). They are value demanding consumers, resilient and creative entrepreneurs, producers, business partners and innovators. They are largely excluded from formal markets. There is a strong demand for innovative products, services and technologies that provide access to basic needs. These markets are growing fast.There are 4.5 billion people in the base of the pyramid as customers, diverse suppliers and strategic distribution and retail partners. These people live primarily in Asia, Africa and South America.
The Bottom of the Economic Pyramid or Base of the Economic Pyramid (BoP) is defined as those people whose earning is less than US$8 per day. This domain is popularly referred as Base of Pyramid (BoP). They are value demanding consumers, resilient and creative entrepreneurs, producers, business partners and innovators. They are largely excluded from formal markets. There is a strong demand for innovative products, services and technologies that provide access to basic needs. These markets are growing fast.There are 4.5 billion people in the base of the pyramid as customers, diverse suppliers and strategic distribution and retail partners. These people live primarily in Asia, Africa and South America. -
Engaging people at the BoP as producers, consumers and entrepreneurs is key to improving their livelihood and driving economic growth for both communities and the private sector.
In total the BoP represents a $ 5 trillion market according to the World Bank Group of which:- $ 2.3 trillion in food and nutrition
•$ 317 billion in energy
•$ 32 billion in water
•$ 508 billion in housing
•$ 206 billion in information & communication technology
•$ 193 billion in education
•$ 243 billion in health
•$ 405 billion in clothing and personal care
•$ 298 billion in transport
Unlike MNCs can involve in these market, inhabitants of these area can be emerged as entrepreneur.
- $ 2.3 trillion in food and nutrition
-
Shaping the BoP Market – Grameen Bank Model
The traditional debt market was driven by mortgage. None was offered any debt or credit without collateral. The Grameen Bank of Bangladesh changed the whole process by the innovative way of addressing the debt recovery cycle. -
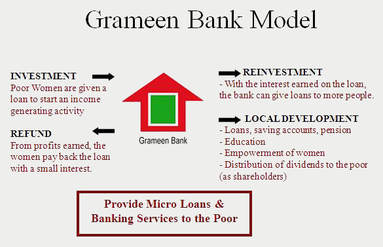
Grameen Bank’s micro credit model
Grameen Bank is founded in 1983 by Government of Bangladesh Ordinance on the belief that people have endless potential, and unleashing their creativity and initiative helps them end poverty. The bank has offered credit to the poor, women, illiterate, and unemployed people – formerly under served. Access to credit is based on reasonable terms, such as the group lending system and weekly-installment payments, with reasonably long terms of loans, enabling the poor to build on their existing skills to earn better income in each cycle of loans.
Professor Yunus developed the principles of micro credit from his research and experience by lending only US $ 27 to poor people at Jubra village near University of Chittagong in 1974.
Grameen’s objective has been to promote financial independence among the poor. Professor Yunus encourages all borrowers – members of the bank to become savers, so that their local capital can be converted into new loans to others.As of 2017, the Bank had about 2,600 branches and nine million borrowers, with a repayment rate of 99.6%. 97% of the borrowers were women. The Bank has been active in 97% of the villages of Bangladesh. Its success has inspired similar projects in more than 40 countries around the world, including a World Bank initiative to finance Grameen-type schemes.
Grameen Bank is now expanding into wealthy countries, as well. As of 2017, Grameen America had 19 branches in eleven US cities. Its nearly 100,000 borrowers were all women.Grameen Bank and its founder Professor Muhammad Yunus jointly awarded Noble Peace Prize in 2006.
-
Nobel Peace Prize laureate Professor Muhammad Yunus described in his books “Creating a world without poverty—Social Business and the future of capitalism” and “Building Social Business—The new kind of capitalism that serves humanity’s most pressing need”
Professor Muhammad Yunus defined a social business as a business:-
- Created and designed to address a social problem
- A non-loss, non-dividend company, i.e.
(1) It is financially self-sustainable and
(2) Profits realized by the business are reinvested in the business itself (or used to start other social businesses), with the aim of increasing social impact, for example expanding the company’s reach, improving the products or services or in other ways subsidizing the social mission.Unlike a profit-maximizing business, the prime aim of a social business is not to maximize profits (although generating profits is desired). Furthermore, business owners are not receiving any dividend out of the business profits, if any.
On the other hand, unlike a non-profit, a social business is not dependent on donations or on private or public grants to survive and to operate, because, as any other business, it is self-sustainable. Furthermore, unlike a non-profit, where funds are spent only once on the field, funds in a social business are invested to increase and improve the business’ operations on the field on an indefinite basis. As per Professor Muhammad Yunus’ quote: “A charity dollar has only one life; a social business dollar can be invested over and over again.”
-
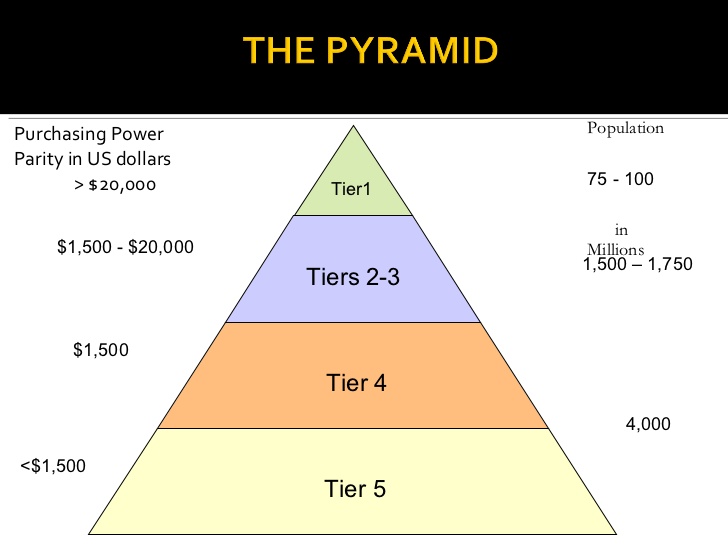
The concept of addressing the needs of the poor through business was introduced in 2006 by Professor Coimbatore Krishnarao Prahalad (born in 8 August 1941, died in 16 April 2010), popularly known as Professor C K Prahalad, in his book ‘The Fortune at the Bottom of the Pyramid – eradicating poverty through profits’.
Hindustan Lever Ltd (HLL, presently Hindustan Unilever – HUL) marketed and distributed single serve mini – pack (sachets) toothpaste, shampoo, soap, ketchup, detergents etc targeting the BoP market. Now, this single serve sachet packs became quite normal in penetrating BoP markets across the globe.
Professor C K Prahalad sketched 12 principles of innovation for BoP markets.


Leave a Reply